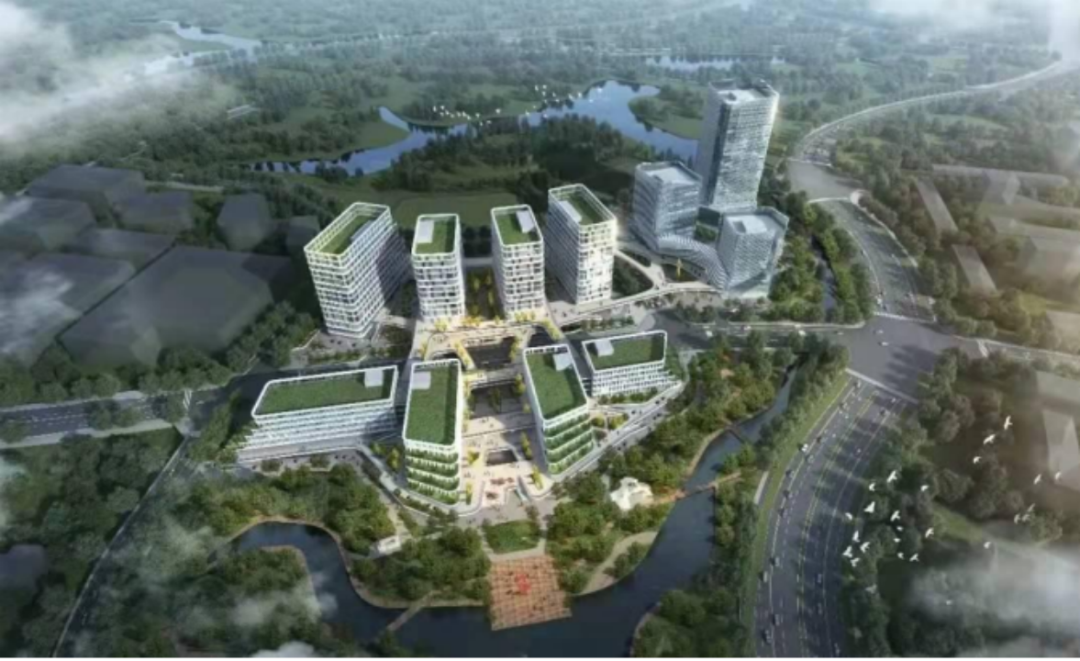
Zhongheng Energy has always regarded serving the “National Energy Security Strategy” as its corporate development responsibility. Upholding the core values of “Five Responsibilities,” the company has deepened its expertise in the field of new energy circular economy. Its Guangdong New Energy Circular Economy Zero-Carbon Smart Industrial Park, a key provincial construction project in Guangdong, aims to utilize green and low-carbon technologies to create a comprehensive demonstration zone integrating green buildings, net-zero carbon parks, and green factories.
The project is anchored by the Greater Bay Area (Guangzhou) Carbon Finance Intelligent Computing Center as its core base. It is strategically deployed across Guangdong, extending its influence throughout South China, with plans to fully open up the national new energy industry carbon asset big data supply chain market within five years. Aligned with China’s “Dual Carbon” strategy and Guangdong Province’s requirements for high-quality green and low-carbon development, the project is positioned around the core principles of “zero carbon, circularity, and intelligence,” aiming to create a comprehensive new energy industrial park that serves as a demonstrative and leading model.

Project Name: Guangdong New Energy Circular Economy Zero-Carbon Smart Industrial Park — Guangzhou Headquarters Project
Developer: Zhongheng Zhilian (Guangzhou) Energy Development Co., Ltd.
Location: Huadu District, Guangzhou
Green & Low-Carbon Certification: Junye Low Carbon
Project Overview:
The Guangdong New Energy Circular Economy Zero-Carbon Smart Industrial Park — Guangzhou Headquarters Project represents a total investment of RMB 1.22 billion. The first phase involves a planned investment of RMB 500 million, utilizing a site of 60 mu (approximately 4 hectares) with a plot ratio of 3.05 and a total floor area of around 120,000 square meters.
Strategically situated within the nationally designated Huadu Chini Industrial Park, an economic and technological development zone, the project encompasses several key functional areas:
Integrated recycling and reuse of 60,000 tons of new energy power batteries
Intelligent manufacturing of 10 GWh of new energy storage systems
A Carbon Neutrality Research Institute
An Academician Workstation and R&D Center
Our company assists the project in setting a new industry benchmark by moving away from homogeneity and emphasizing uniqueness. We adopt a people-oriented approach in implementing green and low-carbon park technologies, striving to develop the project into a nationally recognized green, low-carbon, and smart industrial park. The project has achieved certifications such as Three-Star Green Building, Net Zero Carbon Park, Green Factory, and Zero-Carbon Space, establishing itself as a model demonstration park aligned with China’s “Dual Carbon” strategy. Guided by the core principles of “Zero-Carbon Drive, Circular Empowerment, and Smart Management,” the project aims to create a comprehensive new energy industry hub that integrates green buildings, net-zero carbon operations, green manufacturing, and industrial collaboration.
This project is not only a zero-carbon headquarters base in Guangzhou but also serves as a national demonstration for the “Dual Carbon” goals, a new energy hub in the Greater Bay Area, an engine for Guangzhou’s green economy, and a benchmark for the circular economy. Its successful implementation will advance the construction standards for zero-carbon parks in Guangdong Province and across the nation, forming a sustainable development model that integrates “policy, technology, finance, and industry” into a cohesive framework.
The Guangdong New Energy Circular Economy Zero-Carbon Smart Industrial Park is designed and constructed in strict accordance with national standards: the factory area meets both the “Green Factory” and zero-carbon park criteria, while the office buildings comply with the Three-Star Green Building certification and zero-carbon space requirements.

Process Technology Energy-Saving Measures:
General and pollution control equipment adopts high-efficiency, energy-saving, and low-carbon products. The energy efficiency of major energy-consuming equipment meets the required energy-saving evaluation criteria, with actual operational efficiency or key parameters aligned with economical operation standards. Power supply equipment is positioned as close as possible to load centers or primary consumption points to facilitate operations and enhance production efficiency.
Transportation Vehicle Electrification:
Production vehicles such as forklifts and official cars are transitioned to electric models to reduce carbon emissions from transportation. Charging stations are installed within the park to meet the charging needs of electric vehicles both inside and nearby the park.
Green Electricity Procurement:
The project explores green electricity trading with local power trading centers and retail electricity companies to fulfill the requirement for a high proportion of green electricity usage in the zero-carbon park.
Dual Carbon Management Platform:
Building upon the energy management platform, smart and big data technologies are fully utilized to monitor, track, and provide feedback on the project’s total carbon emissions and intensity in real time. Based on the carbon emission management system framework, modules for benchmarking carbon emission levels, predicting carbon emissions, and operationalizing the carbon emission management system are designed and developed. This enables continuous tracking and evaluation of the synergistic effects of pollution reduction and carbon mitigation resulting from adjustments in the project’s energy structure, thereby enhancing the scientific precision of management. Through terminal data collection and an intelligent information analysis and decision-making system, dynamic monitoring, feedback, early warning, and optimization of carbon emissions, carbon assets, and carbon sinks within the park are achieved. The platform maximizes the use of renewable energy and carbon sink resources and further employs carbon offset measures to achieve ultra-low or even net-zero carbon emissions during the operational phase.

Sponge City Initiative:
Green sponge technologies transform the park into a “breathing” green space. Facilities such as permeable pavement, sunken green spaces, and rain gardens rapidly absorb, infiltrate, and store rainwater, effectively controlling surface runoff. The stored rainwater is reused for park landscaping irrigation and road cleaning, significantly enhancing water resource recycling efficiency.
Technological Innovation: Exploring New Directions for Green Energy Development
Zhongheng Energy, positioned at the forefront of the industry, has initiated projects for the comprehensive recycling and reuse of decommissioned photovoltaic power generation equipment, as well as wind turbine and solid-state battery recycling. By analyzing industry trends and addressing technical challenges, the company explores innovative application pathways, providing strategic support for green energy technological advancements and contributing to the development of a more efficient and sustainable energy system.

02. Benefits of Zero-Carbon Parks (Value)
1. Favorable Financing Costs
Data released by multiple banks on green credit shows that, as reported by 21st Century Business Herald on April 11, 2025, in an article titled “Bank Annual Reports Reveal Green Finance Progress: Growth Rates Generally Slow, Transition Finance Becomes Key to ‘Quality Improvement’,” by the end of 2024, 15 banks continued to increase their green credit allocations, with all achieving positive growth in their green credit balances.
For projects, legally and compliantly leveraging green finance policies not only enables access to low-cost funding but also accelerates the pace of green transformation. This provides advantages in cost reduction, efficiency improvement, priority approval, and policy alignment, allowing projects to gain a competitive edge.

2. Adapting to Green Trade Rules and Gaining Initiative in Foreign Trade
Current carbon emission requirements are increasingly being integrated into international trade rules and supply chain systems. Zero-carbon parks, equipped with traceable energy supply systems and full-process carbon footprint management systems, can significantly reduce product carbon footprints for enterprises and enhance their market competitiveness.
Avoiding High “Carbon Tariffs” (Taking the EU CBAM as an Example):
The European Union’s Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM, commonly known as the “carbon tariff”) is a prime example. Products such as cement, steel, aluminum, fertilizers, electricity, and hydrogen exported to the EU must declare their “embedded carbon emissions” generated during production.The role of the full-process carbon footprint management system here is “self-verification.”
The role of the traceable energy supply system here is “burden reduction.”
Meeting “Green Supply Chain” Requirements of Leading Clients:
Global giants such as Apple, IKEA, Walmart, and Volkswagen have made carbon neutrality commitments and are transmitting this pressure throughout their supply chains. They require suppliers to:Provide Product Carbon Footprint (PCF) data for their products.
Set emission reduction targets and progressively increase the proportion of green electricity usage.
3. Guiding Deep Industrial Decarbonization and Promoting Regional Coordinated Development
Zero-carbon parks serve as platforms to explore the “green manufacturing with green energy” model, guiding traditional industries to pursue deep decarbonization pathways and empowering emerging industries to achieve high-quality green and low-carbon development. By leveraging the comparative advantages of regional industrial development and resource endowments, a coordinated layout of zero-carbon parks can be implemented. This encourages energy-intensive industries to relocate and cluster in parks with adequate resource support, energy security, and environmental capacity. Such an approach fosters rational industrial division and virtuous cycles, achieving a win-win outcome for both ecological and economic benefits.







